
Overview
KubeDB is the Kubernetes Native Database Management Solution which simplifies and automates routine database tasks such as Provisioning, Monitoring, Upgrading, Patching, Scaling, Volume Expansion, Backup, Recovery, Failure detection, and Repair for various popular databases on private and public clouds. The databases that KubeDB supports are Elasticsearch, Kafka, MySQL, MongoDB, MariaDB, Redis, PostgreSQL, ProxySQL, Percona XtraDB, Memcached and PgBouncer. You can find the guides to all the supported databases in KubeDB . KubeDB provides support not only for the official Elasticsearch by Elastic and OpenSearch by AWS, but also other open source distributions like SearchGuard and OpenDistro . KubeDB provides all of these distribution’s support under the Elasticsearch CR of KubeDB. In this tutorial we will deploy Elasticsearch and Kibana in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS). We will cover the following steps:
- Install KubeDB
- Deploy Elasticsearch Topology Cluster
- Deploy Kibana
- Read/Write Data through Kibana
Get Cluster ID
We need the cluster ID to get the KubeDB License. To get cluster ID, we can run the following command:
$ kubectl get ns kube-system -o jsonpath='{.metadata.uid}'
debacab3-y89q-4168-ba24-e97a553dcfa4
Get License
Go to Appscode License Server to get the license.txt file. For this tutorial we will use KubeDB Enterprise Edition.
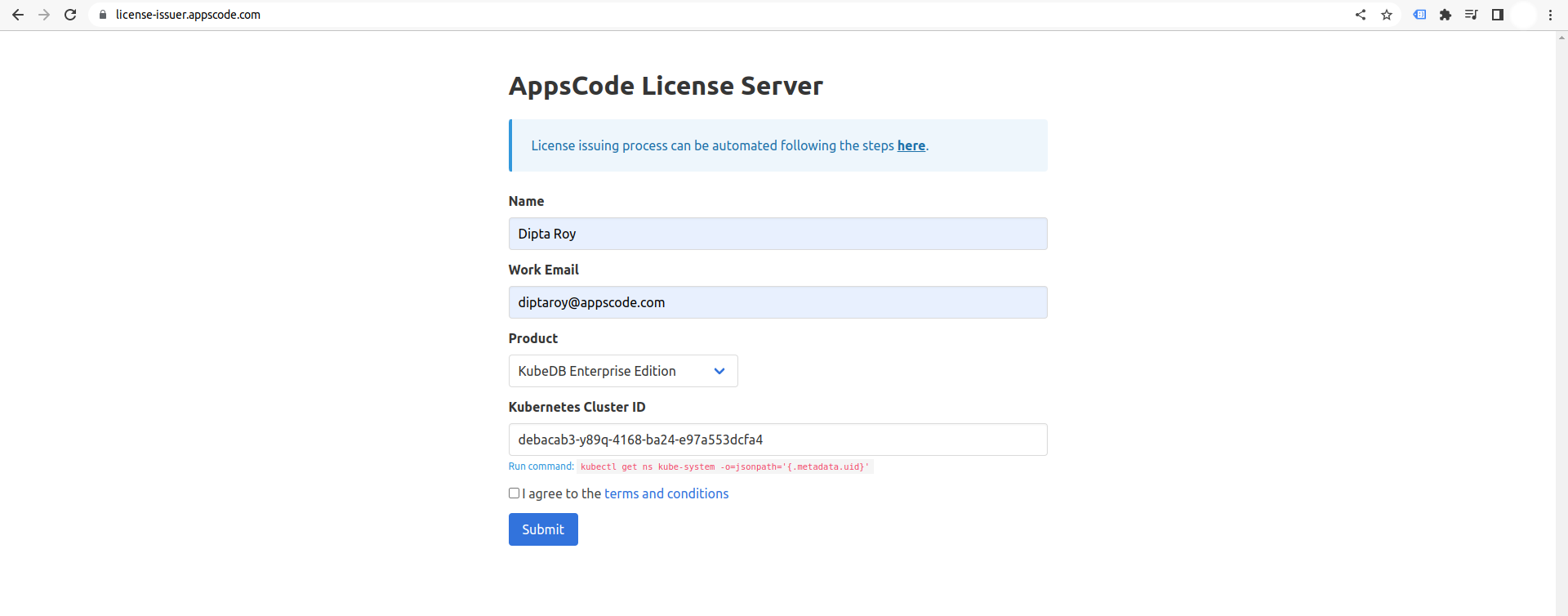
Install KubeDB
We will use helm to install KubeDB. Please install helm here
if it is not already installed.
Now, let’s install KubeDB.
$ helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
$ helm repo update
$ helm search repo appscode/kubedb
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
appscode/kubedb v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB by AppsCode - Production ready databases...
appscode/kubedb-autoscaler v0.19.0 v0.19.0 KubeDB Autoscaler by AppsCode - Autoscale KubeD...
appscode/kubedb-catalog v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB Catalog by AppsCode - Catalog for databa...
appscode/kubedb-community v0.24.2 v0.24.2 KubeDB Community by AppsCode - Community featur...
appscode/kubedb-crds v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB Custom Resource Definitions
appscode/kubedb-dashboard v0.10.0 v0.10.0 KubeDB Dashboard by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-enterprise v0.11.2 v0.11.2 KubeDB Enterprise by AppsCode - Enterprise feat...
appscode/kubedb-grafana-dashboards v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 A Helm chart for kubedb-grafana-dashboards by A...
appscode/kubedb-metrics v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB State Metrics
appscode/kubedb-one v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB and Stash by AppsCode - Production ready...
appscode/kubedb-ops-manager v0.21.0 v0.21.5 KubeDB Ops Manager by AppsCode - Enterprise fea...
appscode/kubedb-opscenter v2023.06.19 v2023.06.19 KubeDB Opscenter by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-provisioner v0.34.0 v0.34.2 KubeDB Provisioner by AppsCode - Community feat...
appscode/kubedb-schema-manager v0.10.0 v0.10.0 KubeDB Schema Manager by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-ui v2023.03.23 0.4.1 A Helm chart for Kubernetes
appscode/kubedb-ui-server v2021.12.21 v2021.12.21 A Helm chart for kubedb-ui-server by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-webhook-server v0.10.0 v0.10.0 KubeDB Webhook Server by AppsCode
# Install KubeDB Enterprise operator chart
$ helm install kubedb appscode/kubedb \
--version v2023.06.19 \
--namespace kubedb --create-namespace \
--set kubedb-provisioner.enabled=true \
--set kubedb-ops-manager.enabled=true \
--set kubedb-autoscaler.enabled=true \
--set kubedb-dashboard.enabled=true \
--set kubedb-schema-manager.enabled=true \
--set-file global.license=/path/to/the/license.txt
Let’s verify the installation:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -l "app.kubernetes.io/instance=kubedb"
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-autoscaler-9cb8dd9bc-rsws9 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-dashboard-6f4d5954bc-xwzrz 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-ops-manager-7cd88994c4-bc5dc 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-provisioner-54867f9dbc-7m2qt 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-schema-manager-6b88f67fc-zmfwj 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-webhook-server-74748f5974-qqfxt 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
We can list the CRD Groups that have been registered by the operator by running the following command:
$ kubectl get crd -l app.kubernetes.io/name=kubedb
NAME CREATED AT
elasticsearchautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:14Z
elasticsearchdashboards.dashboard.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:09Z
elasticsearches.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:09Z
elasticsearchopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:18Z
elasticsearchversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:52Z
etcds.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:19Z
etcdversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:53Z
kafkas.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:29Z
kafkaversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:53Z
mariadbautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:14Z
mariadbdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:10Z
mariadbopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:39Z
mariadbs.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:10Z
mariadbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:53Z
memcacheds.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:20Z
memcachedversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:54Z
mongodbautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:15Z
mongodbdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:07Z
mongodbopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:22Z
mongodbs.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:08Z
mongodbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:54Z
mysqlautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:15Z
mysqldatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:07Z
mysqlopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:36Z
mysqls.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:07Z
mysqlversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:54Z
perconaxtradbautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:15Z
perconaxtradbopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:54Z
perconaxtradbs.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:26Z
perconaxtradbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:55Z
pgbouncers.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:26Z
pgbouncerversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:55Z
postgresautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:15Z
postgresdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:09Z
postgreses.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:09Z
postgresopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:47Z
postgresversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:55Z
proxysqlautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:15Z
proxysqlopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:51Z
proxysqls.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:27Z
proxysqlversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:56Z
publishers.postgres.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:58:04Z
redisautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:16Z
redises.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:28Z
redisopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:43Z
redissentinelautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:16Z
redissentinelopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:58Z
redissentinels.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:57:28Z
redisversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:53:56Z
subscribers.postgres.kubedb.com 2023-08-18T06:58:09Z
Deploy Elasticsearch Topology Cluster
We are going to use the KubeDB-provided Custom Resource object Elasticsearch for deployment. The object will be deployed in demo namespace. So, let’s create the namespace first.
$ kubectl create namespace demo
namespace/demo created
Here is the yaml of Elasticsearch we are going to use:
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: es-cluster
namespace: demo
spec:
enableSSL: true
version: xpack-8.8.0
storageType: Durable
topology:
master:
replicas: 2
resources:
storage:
storageClassName: "gp2"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
data:
replicas: 2
resources:
storage:
storageClassName: "gp2"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
ingest:
replicas: 2
resources:
storage:
storageClassName: "gp2"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Here,
spec.version- is the name of the ElasticsearchVersion CR. Here, we are using Elasticsearch versionxpack-8.8.0of Elasticsearch distribution.spec.enableSSL- specifies whether the HTTP layer is secured with certificates or not.spec.storageType- specifies the type of storage that will be used for Elasticsearch database. It can beDurableorEphemeral. The default value of this field isDurable. IfEphemeralis used then KubeDB will create the Elasticsearch database usingEmptyDirvolume. In this case, you don’t have to specifyspec.storagefield. This is useful for testing purposes.spec.topology- specifies the node-specific properties for the Elasticsearch cluster.spec.terminationPolicyfield is Wipeout means that the database will be deleted without restrictions. It can also be “Halt”, “Delete” and “DoNotTerminate”. Learn More about these checkout Termination Policy .
Let’s deploy the above yaml by the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f es-cluster.yaml
elasticsearch.kubedb.com/es-cluster created
However, KubeDB also provides dedicated node support for other node roles like data_hot, data_warm, data_cold, data_frozen, transform, coordinating, data_content and ml for Topology clustering
.
Once these are handled correctly and the Elasticsearch object is deployed, you will see that the following resources are created:
$ kubectl get all -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/es-cluster-data-0 1/1 Running 0 2m21s
pod/es-cluster-data-1 1/1 Running 0 102s
pod/es-cluster-ingest-0 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
pod/es-cluster-ingest-1 1/1 Running 0 102s
pod/es-cluster-master-0 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
pod/es-cluster-master-1 1/1 Running 0 98s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/es-cluster ClusterIP 10.100.143.63 <none> 9200/TCP 2m26s
service/es-cluster-master ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 2m26s
service/es-cluster-pods ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 2m26s
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/es-cluster-data 2/2 2m23s
statefulset.apps/es-cluster-ingest 2/2 2m24s
statefulset.apps/es-cluster-master 2/2 2m24s
NAME TYPE VERSION AGE
appbinding.appcatalog.appscode.com/es-cluster kubedb.com/elasticsearch 8.8.0 2m24s
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
elasticsearch.kubedb.com/es-cluster xpack-8.8.0 Ready 2m33s
We have successfully deployed Elasticsearch cluster in Amazon EKS.
Deploy Kibana
apiVersion: dashboard.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: ElasticsearchDashboard
metadata:
name: es-cluster-dashboard
namespace: demo
spec:
enableSSL: true
databaseRef:
name: es-cluster
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Note: Elasticsearch Database and Elasticsearch dashboard should have to be deployed in the same namespace. In this tutorial, we use
demonamespace for both cases.
spec.enableSSLspecifies whether the HTTP layer is secured with certificates or not.spec.databaseRef.namerefers to the Elasticsearch database name.spec.terminationPolicyrefers to the strategy to follow during dashboard deletion.Wipeoutmeans that the database will be deleted without restrictions. It can also beDoNotTerminatewhich will cause a restriction to delete the dashboard. Learn More about these Termination Policy .
Let’s deploy the above yaml by the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f es-cluster-dashboard.yaml
elasticsearchdashboard.dashboard.kubedb.com/es-cluster-dashboard created
KubeDB will create the necessary resources to deploy the Elasticsearch dashboard according to the above specification. Let’s wait until the dashboard to be ready to use,
$ watch kubectl get elasticsearchdashboard -n demo
NAME TYPE DATABASE STATUS AGE
es-cluster-dashboard dashboard.kubedb.com/v1alpha1 es-cluster Ready 2m2s
Here, Elasticsearch Dashboard is in Ready state.
Connect with Elasticsearch Dashboard
We will use port forwarding
to connect with our Elasticsearch database. Then we will use curl to send HTTP requests to check cluster health to verify that our Elasticsearch database is working well.
Port-forward the Service
KubeDB will create few Services to connect with the database. Let’s check the Services by following command,
$ kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
es-cluster ClusterIP 10.100.143.63 <none> 9200/TCP 6m52s
es-cluster-dashboard ClusterIP 10.100.83.158 <none> 5601/TCP 3m9s
es-cluster-master ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 6m52s
es-cluster-pods ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 6m52s
Here, we are going to use es-cluster-dashboard Service to connect with the database. Now, let’s port-forward the es-cluster-dashboard Service to the port 5601 to local machine:
$ kubectl port-forward -n demo service/es-cluster-dashboard 5601
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:5601 -> 5601
Forwarding from [::1]:5601 -> 5601
Now, our Elasticsearch cluster dashboard is accessible at https://localhost:5601.
Export the Credentials
KubeDB also create some Secrets for the database. Let’s check which Secrets have been created by KubeDB for our es-cluster.
$ kubectl get secret -n demo | grep es-cluster
es-cluster-apm-system-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m46s
es-cluster-beats-system-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m46s
es-cluster-ca-cert kubernetes.io/tls 2 7m49s
es-cluster-client-cert kubernetes.io/tls 3 7m48s
es-cluster-config Opaque 1 7m48s
es-cluster-dashboard-ca-cert kubernetes.io/tls 2 4m6s
es-cluster-dashboard-config Opaque 2 4m6s
es-cluster-dashboard-server-cert kubernetes.io/tls 3 4m6s
es-cluster-elastic-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m48s
es-cluster-http-cert kubernetes.io/tls 3 7m48s
es-cluster-kibana-system-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m46s
es-cluster-logstash-system-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m46s
es-cluster-remote-monitoring-user-cred kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 7m46s
es-cluster-token-gzbxb kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 7m50s
es-cluster-transport-cert kubernetes.io/tls 3 7m49s
Now, we can connect to the database with es-cluster-elastic-cred which contains the admin credentials to connect with the database.
Accessing Database Through Dashboard
To access the database through Dashboard, we have to get the credentials. We can do that by following command,
$ kubectl get secret -n demo es-cluster-elastic-cred -o jsonpath='{.data.username}' | base64 -d
elastic
$ kubectl get secret -n demo es-cluster-elastic-cred -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 -d
MRTdyI(NmciRfU3J
Now, let’s go to https://localhost:5601 from our browser and login by using those credentials.
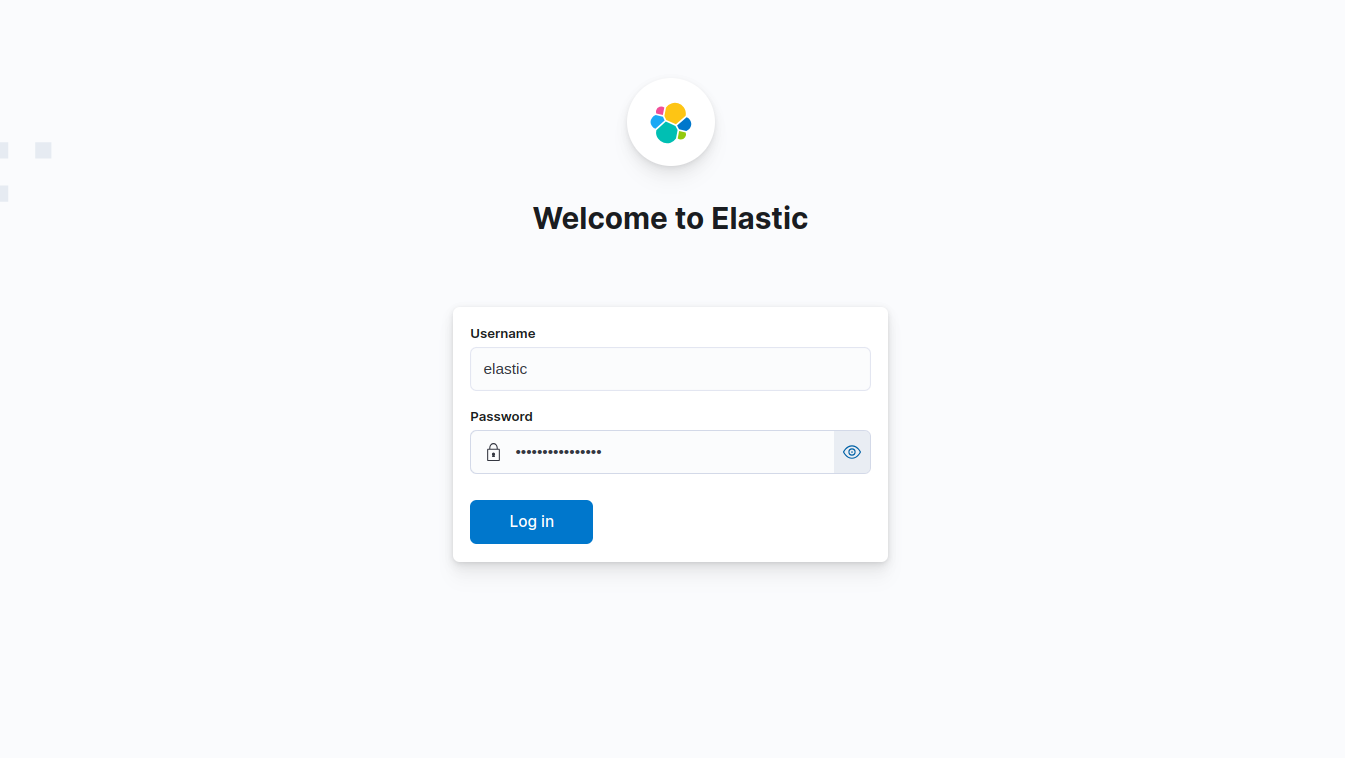
After login successfully, we will see Elasticsearch Dashboard UI. Now, We are going to Dev tools for running some queries into our Elasticsearch database.
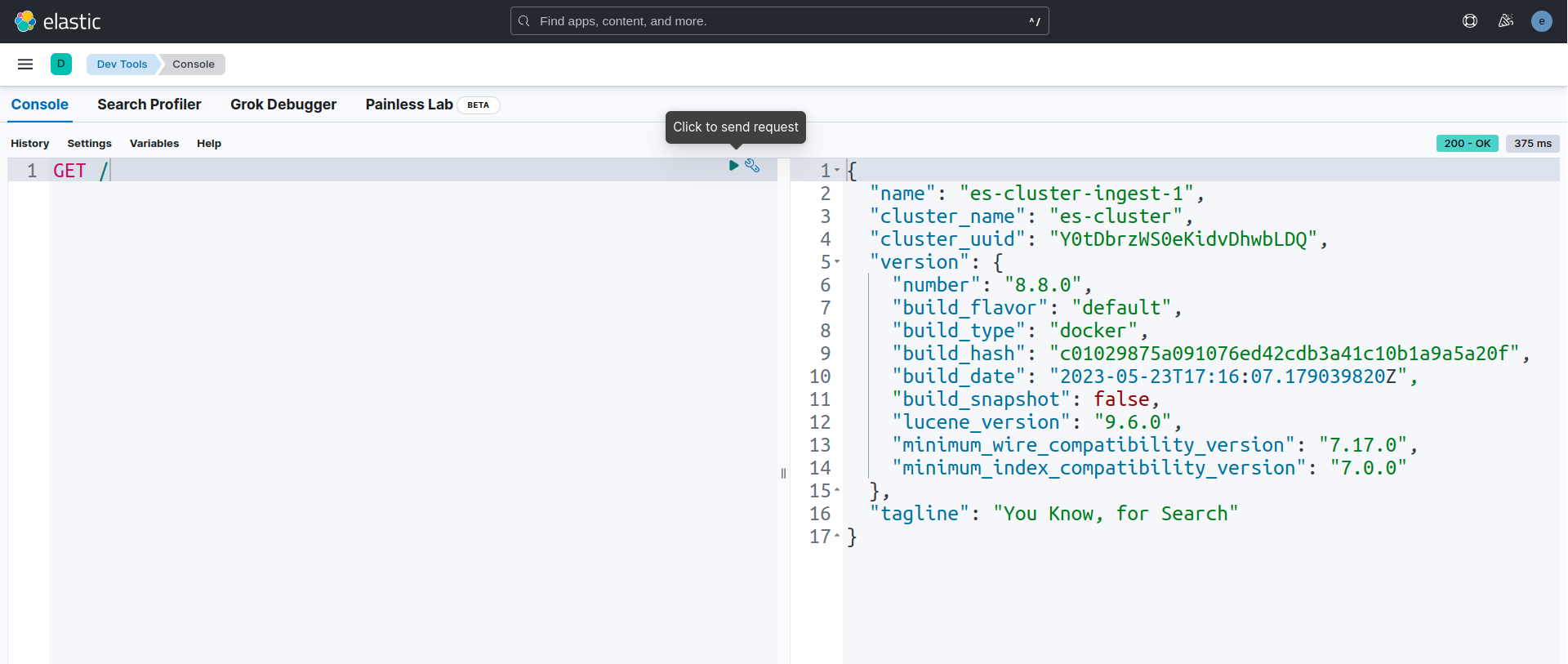
Here, in Dev tools we will use Console section for running some queries. Let’s run GET / query to check node informations.
GET /
Now, we are going to insert some sample data to our Elasticsearch cluster index music/_doc/1 by using PUT query.
PUT music/_doc/1
{
"Playlist": {
"Song": "500 Miles Away from Home",
"Artist": "Bobby Bare"
}
}
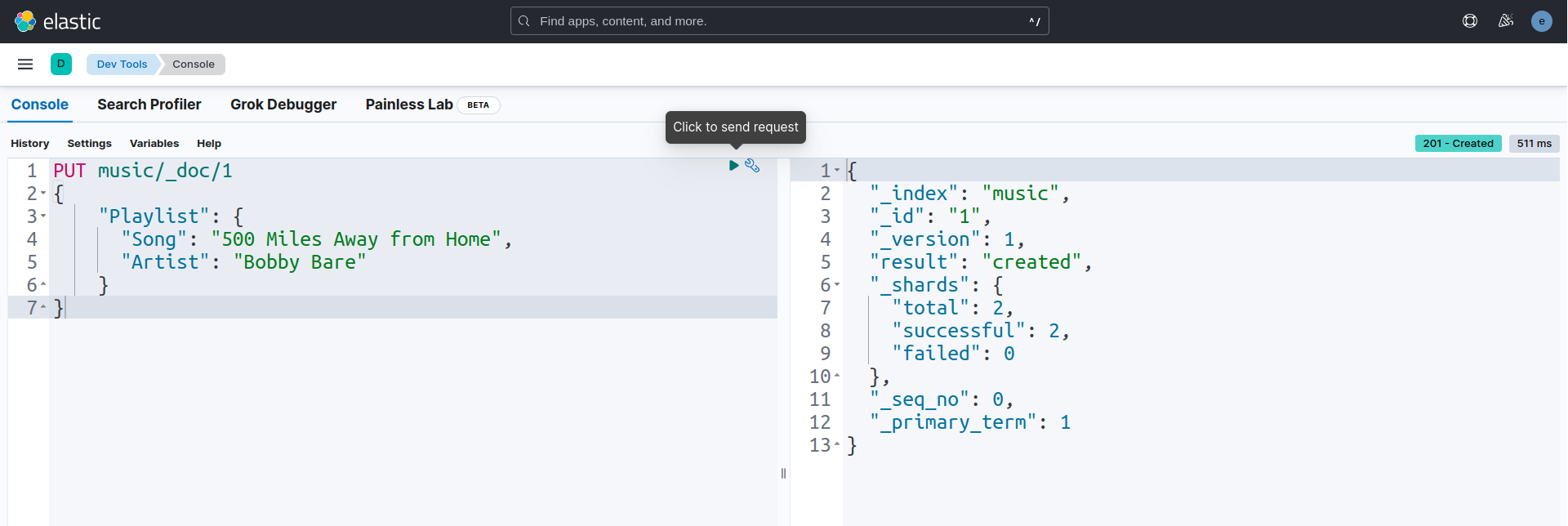
Let’s check that sample data in the index music/_doc/1 by using GET query.
GET music/_doc/1
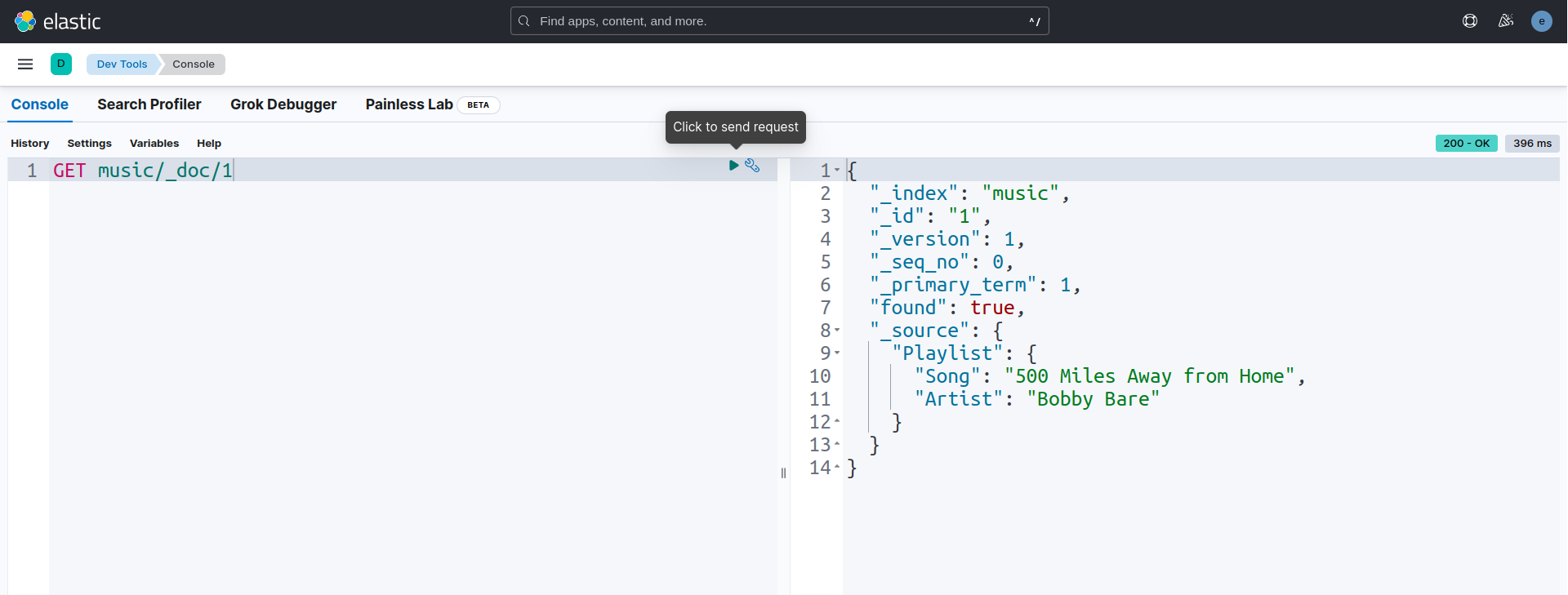
Now, we are going to update sample data in the index music/_doc/1 by using POST query.
POST music/_doc/1
{
"Playlist": {
"Song": "500 Miles Away from Home",
"Artist": "Bobby Bare",
"Released": "September 1963"
}
}
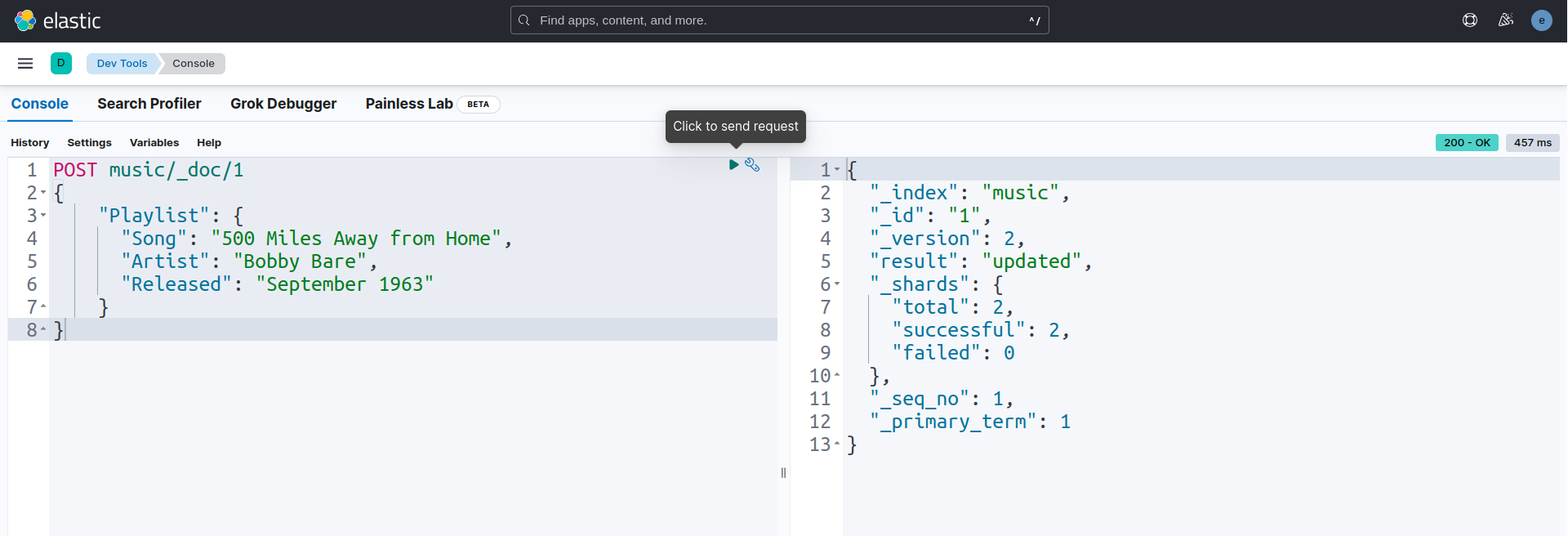
Let’s verify the index music/_doc/1 again to see whether the data is updated or not.
GET music/_doc/1
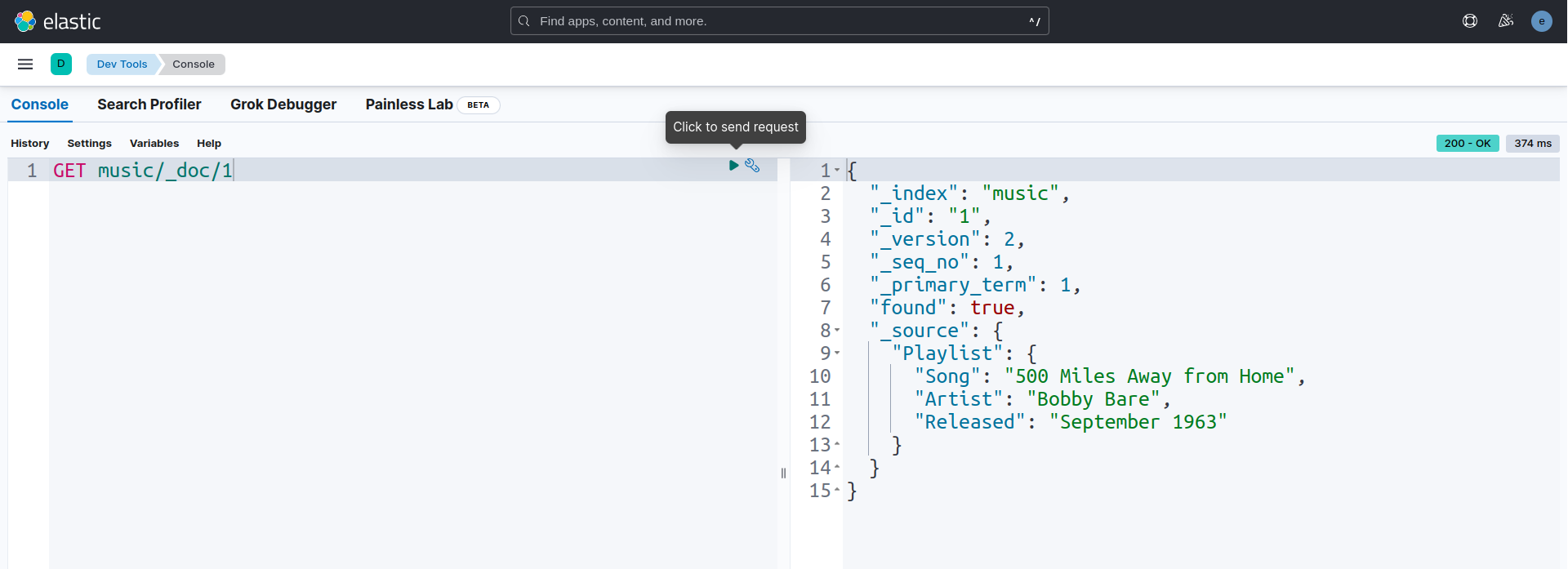
We have made an in depth tutorial on Elasticsearch Hot Warm Cold Architecture Management with Kibana in Kubernetes Using KubeDB. You can have a look into the video below:
Support
To speak with us, please leave a message on our website .
To receive product announcements, follow us on Twitter .
To watch tutorials of various Production-Grade Kubernetes Tools Subscribe our YouTube channel.
More about Elasticsearch in Kubernetes
If you have found a bug with KubeDB or want to request for new features, please file an issue .










