Overview
KubeDB is the Kubernetes Native Database Management Solution which simplifies and automates routine database tasks such as Provisioning, Monitoring, Upgrading, Patching, Scaling, Volume Expansion, Backup, Recovery, Failure detection, and Repair for various popular databases on private and public clouds. The databases supported by KubeDB include MongoDB, Elasticsearch, MySQL, MariaDB, Redis, PostgreSQL, Percona XtraDB, and Memcached. Additionally, KubeDB also supports ProxySQL, PgBouncer, and the streaming platform Kafka. You can find the guides to all the supported databases in KubeDB . In this tutorial we will show Vertical scaling of MySQL cluster in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). We will cover the following steps:
- Install KubeDB
- Deploy MySQL Cluster
- Read/Write Sample Data
- Vertical Scaling of MySQL Cluster
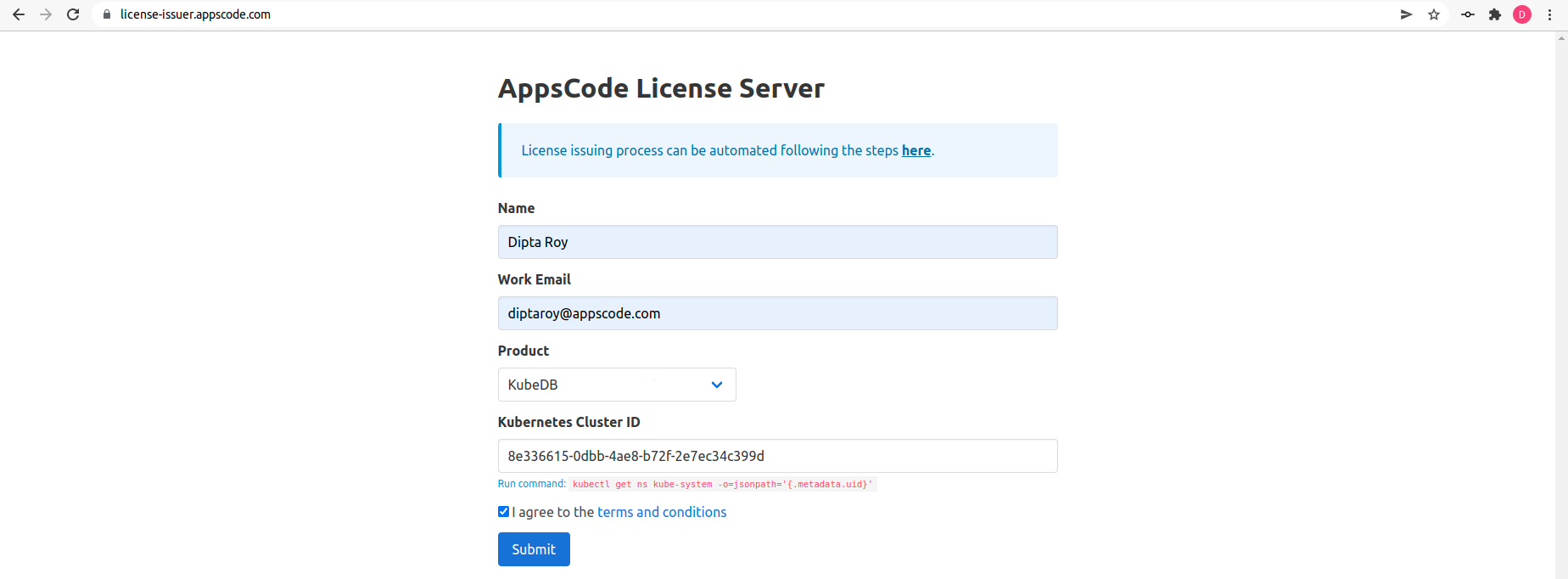
Get Cluster ID
We need the cluster ID to get the KubeDB License. To get cluster ID, we can run the following command:
$ kubectl get ns kube-system -o jsonpath='{.metadata.uid}'
8e336615-0dbb-4ae8-b72f-2e7ec34c399d
Get License
Go to Appscode License Server to get the license.txt file. For this tutorial we will use KubeDB.
Install KubeDB
We will use helm to install KubeDB. Please install helm here
if it is not already installed.
Now, let’s install KubeDB.
$ helm search repo appscode/kubedb
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
appscode/kubedb v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeDB by AppsCode - Production ready databases...
appscode/kubedb-autoscaler v0.27.0 v0.27.0 KubeDB Autoscaler by AppsCode - Autoscale KubeD...
appscode/kubedb-catalog v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeDB Catalog by AppsCode - Catalog for databa...
appscode/kubedb-community v0.24.2 v0.24.2 KubeDB Community by AppsCode - Community featur...
appscode/kubedb-crd-manager v0.0.5 v0.0.5 KubeDB CRD Manager by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-crds v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeDB Custom Resource Definitions
appscode/kubedb-dashboard v0.18.0 v0.18.0 KubeDB Dashboard by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-enterprise v0.11.2 v0.11.2 KubeDB Enterprise by AppsCode - Enterprise feat...
appscode/kubedb-grafana-dashboards v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 A Helm chart for kubedb-grafana-dashboards by A...
appscode/kubedb-kubestash-catalog v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeStash Catalog by AppsCode - Catalog of Kube...
appscode/kubedb-metrics v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeDB State Metrics
appscode/kubedb-one v2023.12.28 v2023.12.28 KubeDB and Stash by AppsCode - Production ready...
appscode/kubedb-ops-manager v0.29.0 v0.29.0 KubeDB Ops Manager by AppsCode - Enterprise fea...
appscode/kubedb-opscenter v2024.2.14 v2024.2.14 KubeDB Opscenter by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-provider-aws v2024.2.14 v0.4.0 A Helm chart for KubeDB AWS Provider for Crossp...
appscode/kubedb-provider-azure v2024.2.14 v0.4.0 A Helm chart for KubeDB Azure Provider for Cros...
appscode/kubedb-provider-gcp v2024.2.14 v0.4.0 A Helm chart for KubeDB GCP Provider for Crossp...
appscode/kubedb-provisioner v0.42.0 v0.42.0 KubeDB Provisioner by AppsCode - Community feat...
appscode/kubedb-schema-manager v0.18.0 v0.18.0 KubeDB Schema Manager by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-ui v2024.2.13 0.6.4 A Helm chart for Kubernetes
appscode/kubedb-ui-server v2021.12.21 v2021.12.21 A Helm chart for kubedb-ui-server by AppsCode
appscode/kubedb-webhook-server v0.18.0 v0.18.0 KubeDB Webhook Server by AppsCode
$ helm install kubedb oci://ghcr.io/appscode-charts/kubedb \
--version v2024.2.14 \
--namespace kubedb --create-namespace \
--set-file global.license=/path/to/the/license.txt \
--wait --burst-limit=10000 --debug
Let’s verify the installation:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -l "app.kubernetes.io/instance=kubedb"
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-autoscaler-6458894494-g79nh 1/1 Running 0 5m29s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-ops-manager-66669d4f9f-48dsb 1/1 Running 0 5m29s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-provisioner-6df5bf65c8-hpjrn 1/1 Running 0 5m29s
kubedb kubedb-kubedb-webhook-server-5447789b9-mhv6r 1/1 Running 0 5m29s
kubedb kubedb-sidekick-5dc87959b7-582vb 1/1 Running 0 5m29s
We can list the CRD Groups that have been registered by the operator by running the following command:
$ kubectl get crd -l app.kubernetes.io/name=kubedb
NAME CREATED AT
connectclusters.kafka.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:49Z
connectors.kafka.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:49Z
druidversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
elasticsearchautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:46Z
elasticsearchdashboards.elasticsearch.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:46Z
elasticsearches.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:46Z
elasticsearchopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:46Z
elasticsearchversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
etcdversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
ferretdbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
kafkaconnectorversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
kafkaopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:49Z
kafkas.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:49Z
kafkaversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
mariadbautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:52Z
mariadbdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:53Z
mariadbopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:52Z
mariadbs.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:52Z
mariadbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
memcachedversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
mongodbarchivers.archiver.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:56Z
mongodbautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:56Z
mongodbdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:56Z
mongodbopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:56Z
mongodbs.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:56Z
mongodbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
mysqlarchivers.archiver.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:59Z
mysqlautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:59Z
mysqldatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:00Z
mysqlopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:59Z
mysqls.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:34:59Z
mysqlversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
perconaxtradbversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
pgbouncerversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
pgpoolversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
postgresarchivers.archiver.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
postgresautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
postgresdatabases.schema.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
postgreses.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
postgresopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
postgresversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
proxysqlversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:56Z
publishers.postgres.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
rabbitmqversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:57Z
redisautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redises.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redisopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redissentinelautoscalers.autoscaling.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redissentinelopsrequests.ops.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redissentinels.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:06Z
redisversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:57Z
singlestoreversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:57Z
solrversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:57Z
subscribers.postgres.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:35:03Z
zookeeperversions.catalog.kubedb.com 2024-02-20T04:33:57Z
Deploy MySQL Cluster
We are going to Deploy MySQL Cluster using KubeDB. First, let’s create a Namespace in which we will deploy the database.
$ kubectl create namespace demo
namespace/demo created
Here is the yaml of the MySQL CR we are going to use:
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: MySQL
metadata:
name: mysql-cluster
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "8.2.0"
replicas: 3
topology:
mode: GroupReplication
storageType: Durable
storage:
storageClassName: "default"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Let’s save this yaml configuration into mysql-cluster.yaml
Then create the above MySQL CR,
$ kubectl apply -f mysql-cluster.yaml
mysql.kubedb.com/mysql-cluster created
In this yaml,
- In this yaml we can see in the
spec.versionfield specifies the version of MySQL. Here, we are using MySQL8.2.0. You can list the KubeDB supported versions of MySQL by running$ kubectl get mysqlversionscommand. spec.topologyrepresents the clustering configuration for MySQL.spec.topology.modespecifies the mode for MySQL cluster. Here we have usedGroupReplication.spec.storage.storageClassNameis the name of the StorageClass used to provision PVCs.spec.terminationPolicyfield is Wipeout means that the database will be deleted without restrictions. It can also be “Halt”, “Delete” and “DoNotTerminate”. Learn More about these checkout Termination Policy .
Once these are handled correctly and the MySQL object is deployed, you will see that the following objects are created:
$ kubectl get all -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/mysql-cluster-0 2/2 Running 0 2m9s
pod/mysql-cluster-1 2/2 Running 0 74s
pod/mysql-cluster-2 2/2 Running 0 62s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/mysql-cluster ClusterIP 10.96.155.200 <none> 3306/TCP 2m13s
service/mysql-cluster-pods ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 2m13s
service/mysql-cluster-standby ClusterIP 10.96.18.57 <none> 3306/TCP 2m13s
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/mysql-cluster 3/3 2m9s
NAME TYPE VERSION AGE
appbinding.appcatalog.appscode.com/mysql-cluster kubedb.com/mysql 8.2.0 2m9s
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mysql.kubedb.com/mysql-cluster 8.2.0 Ready 2m13s
Let’s check if the database is ready to use,
$ kubectl get mysql -n demo mysql-cluster
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mysql-cluster 8.2.0 Ready 3m3s
We have successfully deployed MySQL cluster in AKS. Now we can exec into the container to use the database.
Accessing Database Through CLI
To access the database through CLI, we have to get the credentials to access. KubeDB will create Secret and Service for the database mysql-cluster that we have deployed. Let’s check them using the following commands,
$ kubectl get secret -n demo -l=app.kubernetes.io/instance=mysql-cluster
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
mysql-cluster-auth kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 3m18s
$ kubectl get service -n demo -l=app.kubernetes.io/instance=mysql-cluster
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mysql-cluster ClusterIP 10.96.155.200 <none> 3306/TCP 3m37s
mysql-cluster-pods ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 3m37s
mysql-cluster-standby ClusterIP 10.96.18.57 <none> 3306/TCP 3m37s
Now, we are going to use mysql-cluster-auth to get the credentials.
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo mysql-cluster-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.username}' | base64 -d
root
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo mysql-cluster-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 -d
2mK56J2W9MXH9Mpu
Insert Sample Data
In this section, we are going to login into our MySQL database pod and insert some sample data.
$ kubectl exec -it mysql-cluster-0 -n demo -c mysql -- bash
bash-4.4$ mysql --user=root --password='2mK56J2W9MXH9Mpu'
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 134
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE Music;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE TABLE Music.Artist (id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(50), Song VARCHAR(50));
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.02 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO Music.Artist (Name, Song) VALUES ("Bobby Bare", "Five Hundred Miles");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM Music.Artist;
+----+------------+--------------------+
| id | Name | Song |
+----+------------+--------------------+
| 1 | Bobby Bare | Five Hundred Miles |
+----+------------+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
We’ve successfully inserted some sample data to our database. More information about Deploy & Manage MySQL on Kubernetes can be found in Kubernetes MySQL
Vertical Scaling of MySQL Cluster
Vertical Scale Up
We are going to scale up the resources of the MySQL cluster. Before applying Vertical Scaling, let’s check the current resources.
$ kubectl get pod -n demo mysql-cluster-0 -o json | jq '.spec.containers[].resources'
{
"limits": {
"memory": "1Gi"
},
"requests": {
"cpu": "500m",
"memory": "1Gi"
}
}
Create MySQLOpsRequest
In order to scale up, we have to create a MySQLOpsRequest, Let’s create it using this following yaml,
apiVersion: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: MySQLOpsRequest
metadata:
name: vertical-scale-up
namespace: demo
spec:
type: VerticalScaling
databaseRef:
name: mysql-cluster
verticalScaling:
mysql:
resources:
requests:
memory: "1200Mi"
cpu: "0.7"
limits:
memory: "1200Mi"
cpu: "0.7"
In this yaml,
spec.databaseRef.namespecifies that we are performing vertical scaling operation onmysql-clusterdatabase.spec.typespecifies that we are performingVerticalScalingon our database.spec.VerticalScaling.mysqlspecifies the expected mysql container resources after scaling.
Let’s save this yaml configuration into vertical-scale-up.yaml and apply it,
$ kubectl apply -f vertical-scale-up.yaml
mysqlopsrequest.ops.kubedb.com/vertical-scale-up created
Let’s wait for MySQLOpsRequest STATUS to be Successful. Run the following command to watch MySQLOpsRequest CR,
$ watch kubectl get mysqlopsrequest -n demo
NAME TYPE STATUS AGE
vertical-scale-up VerticalScaling Successful 3m52s
From the above output we can see that the MySQLOpsRequest has succeeded. Now, we are going to verify the current resources,
$ kubectl get pod -n demo mysql-cluster-0 -o json | jq '.spec.containers[].resources'
{
"limits": {
"cpu": "700m",
"memory": "1200Mi"
},
"requests": {
"cpu": "700m",
"memory": "1200Mi"
}
}
From all the above outputs we can see that the resources of the cluster is now increased. That means we have successfully scaled up the resources of the MySQL cluster.
Vertical Scale Down
Now, we are going to scale down the resources of the cluster.
Create MySQLOpsRequest
In order to scale down, again we need to create a new MySQLOpsRequest. Let’s create it using this following yaml,
apiVersion: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: MySQLOpsRequest
metadata:
name: vertical-scale-down
namespace: demo
spec:
type: VerticalScaling
databaseRef:
name: mysql-cluster
verticalScaling:
mysql:
resources:
requests:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "0.5"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "0.5"
In this yaml,
spec.databaseRef.namespecifies that we are performing vertical scaling operation onmysql-clusterdatabase.spec.typespecifies that we are performingVerticalScalingon our database.spec.VerticalScaling.mysqlspecifies the expected mysql container resources after scaling.
Let’s save this yaml configuration into vertical-scale-down.yaml and apply it,
$ kubectl apply -f vertical-scale-down.yaml
mysqlopsrequest.ops.kubedb.com/vertical-scale-down created
Let’s wait for MySQLOpsRequest STATUS to be Successful. Run the following command to watch MySQLOpsRequest CR,
$ watch kubectl get mysqlopsrequest -n demo
NAME TYPE STATUS AGE
vertical-scale-down VerticalScaling Successful 5m41s
From the above output we can see that the MySQLOpsRequest has succeeded. Now, we are going to verify the resources,
$ kubectl get pod -n demo mysql-cluster-0 -o json | jq '.spec.containers[].resources'
{
"limits": {
"cpu": "500m",
"memory": "1Gi"
},
"requests": {
"cpu": "500m",
"memory": "1Gi"
}
}
From all the above outputs we can see that the resources of the cluster is decreased. That means we have successfully scaled down the resources of the MySQL cluster.
If you want to learn more about Production-Grade MySQL on Kubernetes you can have a look into that playlist below:
Support
To speak with us, please leave a message on our website .
To receive product announcements, follow us on Twitter/X .
To watch tutorials of various Production-Grade Kubernetes Tools Subscribe our YouTube channel.
More about MySQL on Kubernetes
If you have found a bug with KubeDB or want to request for new features, please file an issue .










